 2018-02-02
2018-02-02  1962
1962
The shift gas means that the synthesis gas enters the shift reactor and reacts the CO with water vapor therein to produce CO2 and hydrogen under the action of the catalyst, so the general shift gas contains hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, small molecular hydrocarbons, hydrogen sulfide, etc.
The effect of H2S in the shift gas on subsequent processes:
1. Effect on decarburization and copper washing process. Decarburization system has strict requirements on H2S in gases. Sulfur H2S entering the decarbonization system of propylene carbonate (PC for short) and polyethylene glycol dimethyl ether (NHD for short), it will not only pollute the decarburization liquid and affect the decarburization efficiency, but also generate sulfur in the air stripping process. Especially when the system solution contains a small amount of iron ions, the reaction of H2S oxidation to sulfur can be accelerated. Sulfur and oil pollution, mechanical impurities form a thick scale layer, attached to the pipe wall of lean solution water cooler, affect the heat transfer, and even block the heat exchanger pipe; sulfur deposits on the filler surface cause plugging of the filler. It is required that the ratio of pentavalent vanadium to tetravalent vanadium should be kept within a certain range when vanadium is used as a corrosion inhibitor in activated hot potash decarburization system. When H2S enters the solution, the pentavalent vanadium content in the solution decreases and the tetravalent vanadium content increases, which weakens the anti-corrosive performance of the solution and even causes the corrosion of the carbon steel to increase, resulting in foaming of the solution and increased vanadium consumption. The copper ammonia solution absorbs H2S to form CuS precipitates, which not only increases copper consumption, but also causes solution viscosity increase, foaming property enhancement and damage to the normal operation of copper washing system because the particles of the precipitate suspended in solution are very fine. These may lead to excessive outlet gas or even with copper liquid, thus causing great harm to production.
2. Effects on methanation catalysts Sulfur is the most important poison of methanation catalyst, and its toxicity to methanation catalyst is cumulative. If the sulfur content in the gas phase is 0.11×10-6, the life of the catalyst can be shortened.
3. Effects on methanol catalysts Sulfur has more toxic effect on copper-zinc methanol synthesis catalyst, and the effect on catalyst life is very significant. Tests have been carried out on two 1L-volume devices using factory gas as desulfurizer and non-desulfurizer on the service life of the combined methanol catalyst, the results show that the life of catalyst after desulfurization is more than 4 times longer.
4. Effects on ammonia synthesis catalysts Sulfide can destroy the active center ofα-Fe in ammonia synthesis catalyst, and make the catalyst deactivation rapidly. The sulfur poisoning of ammonia synthesis catalyst is permanent. It is recommended to remove H2S from the shift gas by activated carbon.
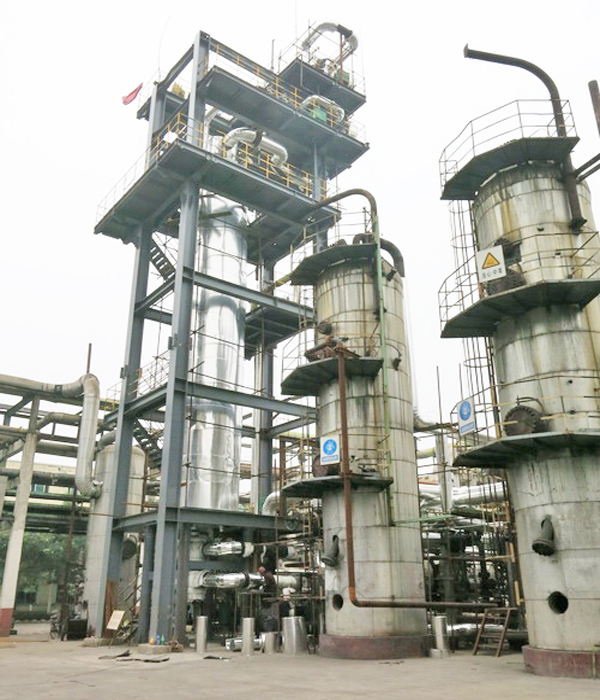

 Current location:Home - Business Scope - Area of application
Current location:Home - Business Scope - Area of application



 Sales hot-line:0816-3736605
Sales hot-line:0816-3736605 E-mail:jysongwei@126.com
E-mail:jysongwei@126.com Address:No. 772, Laojun Road, Jiangyou, Sichuan
Address:No. 772, Laojun Road, Jiangyou, Sichuan

 QQ
QQ Tel
Tel Message
Message Share
Share Top
Top